

The Future is Now: Predictive Maintenance and Industry 4.0
A Trariti Consulting Group Study by Kirti Sachdeva
The Future is Now: Predictive Maintenance and Industry 4.0
Industries are motivated to increase the performance and efficiency of their production lines in the present economic environment, which is characterized by intense globalization and markets with higher expectations, to boost their competitiveness and please their consumers. Industry 4.0 is the result of connectivity, data, new gadgets, inventory reduction, customization, and controlled manufacturing. It now appears unstoppable.
By introducing cognitive automation and subsequently putting the idea of intelligent production into practice, the Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data technologies, as well as the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) methods and cyber-physical systems (CPS), play an important role in this context. This results in intelligent products and services. Companies can tackle the demands of a much more dynamic environment thanks to this creative strategy.
With the prediction of data gathered by numerous sensors on equipment, predictive maintenance has emerged as a viable strategy for extending the life of the equipment. Due to the intricacy of linkages between various production activities in expanding manufacturing ecosystems, it has reached crucial relevance for industries.

Industry 4.0:
The first Industrial Revolution was driven by steam, the second by electricity, the third by early automation and machinery, and the fourth is being shaped by cyber-physical systems or intelligent computers.
Before 2014, "Industry 4.0" was hardly ever used in Google searches, but by 2019, 68 percent of those who participated in a global McKinsey poll considered Industry 4.0 to be a key strategic priority. Seventy percent of respondents claimed their organizations were already testing out or using new technology.
Industry 4.0 is transforming how businesses create, enhance, and distribute their products. By allowing equipment intercommunication through the Internet of Things, Big Data, computer intelligence, and decision-making systems, it has fundamentally changed the industrial and manufacturing sector. This digital technology will enable businesses to respond more quickly to market developments, provide more individualized products, and boost operational efficiency owing to educated Big Data that aids in the more effective and productive production of commodities along the value chain. They give instantaneous information on the state of the machines, such as the location of leaks and their rate of operation.
As it replicates the information obtained in real-time across the manufacturing and supply chain, this technology allows the implementation of smart industries. Several elements, including Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems and physical network systems, are necessary for the data collecting, processing, and storage to take advantage of these advancements. In reality, Industry 4.0 equipment is capable of autonomous communication with one another, enabling it to coordinate with other remote systems as well as with one another through the Internet.

Using the elements of this fourth industrial revolution results in a maintenance plan that seeks to increase the equipment's usable life while lowering costs through ongoing and immediate communication between various machines/equipment in the production or supply chain. Predictive maintenance, which aims to use modern technology to alter scenarios and prevent any kind of breakdown or anomaly through prediction, the reduction of expenses, and the reduction of downtimes, is one of the industry's fundamental pillars.

In light of the fundamental knowledge of the fourth industrial revolution that has been provided, as well as some of its defining characteristics, it is crucial to look at the causes of the security issues that hinder Industry 4.0 and its human component.

There is a considerable rise in unforeseen security breaches has been brought on by cloud-based systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and the interconnection of smart businesses. Industry 4.0's digitalized and networked corporate operations make it more susceptible to cyber espionage or cyber sabotage. We are currently seeing the emergence of highly skilled, well-organized gangs of cybercriminals that are used to prey on particular businesses to steal confidential data and intellectual property.
The issue with this phenomenon extends beyond its effects on sales and also involves harm to the organization's reputation, knowledge loss, and a decline in the competitiveness of those firms that are impacted. Some of them are:
-
Cybersecurity:
The danger of cyberattacks rises as more gadgets are linked to the internet. Operational technology (OT) and industrial control systems (ICS) are particularly vulnerable because they frequently use out-of-date software and protocols that hackers may readily attack.
-
Data security:
Industry 4.0 produces a tonne of data, most of which private and sensitive. Thus, it is crucial to protect the privacy of sensitive data since a breach might cause paramount financial and reputational harm.
-
Security of supply chains:
Given that Industry 4.0 depends on linked networks and supply chains, network security is crucial. The security of the entire system might be jeopardized by a single weak link in the supply chain.
-
Human error:
Industry 4.0 technologies mainly rely on automation, which lessens the need for human interaction. Nonetheless, as employees may unintentionally add vulnerabilities or disregard security procedures, human error continues to be a threat.
-
Physical security:
When robots and automation are used more often, physical security is now an issue. Robbery or damage to robots or other automated equipment might lead to sizable financial losses and halt production.
Predictive Measurement Tools and Material:
Tools for predictive measurement are a form of cutting-edge technology that may have been used to forecast future results based on historical data. Predictive measuring instruments can be used to plan for production schedule optimization and quality control in manufacturing and other industrial contexts.
-
Machine Learning (ML) Methods
Predictive analytics and machine learning can offer a solution for organizations that are swamped with data but face issues turning it into insightful information. Regardless of how much data a company possesses, if it cannot use it to improve internal and external operations and achieve its goals, the data is a meaningless resource.
A recent study by Gartner in 2021 about the Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence shows how Machine Learning has been at the peak of inflated expectations for the past 2- 5 years.
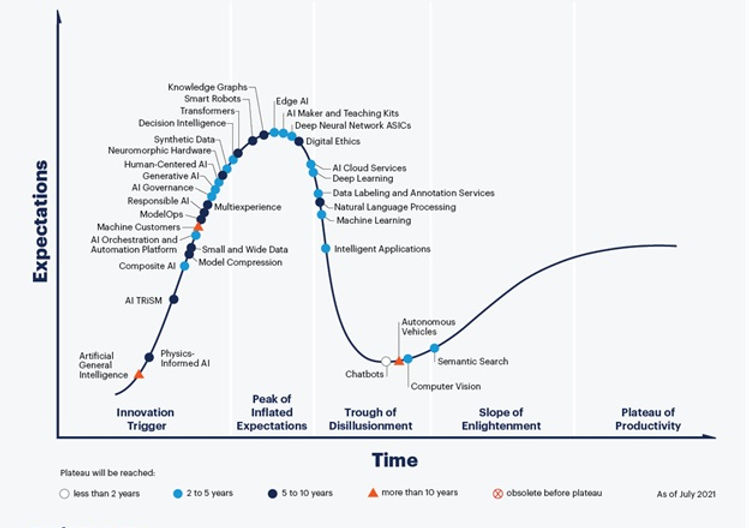
For instance, predictive analytics and machine learning are combined in the banking and financial services sector to detect and decrease fraud, assess market risk, spot opportunities, and much more.
It should come as no surprise that predictive analytics and machine learning play a crucial role in security, with cybersecurity at the top of every company's agenda. Predictive analytics is generally implied by organizations to increase data security, detect abnormalities, and frauds, and improve services and performance.
-
Real-time Monitoring Systems
Although there are countless uses for predictive analytics, engineers may start by using analytics to track the dependability and efficiency of factory sensors.

In addition to providing a soiled data foundation for digital transformation and continuous improvement projects, bad sensor data can result in lost goods, downtime, compliance problems, safety hazards, and more. Good data must be available for industrial enterprises to use for operations, ad hoc analysis, and enterprise analytics.
-
Quality Control:
Predictive measuring techniques can enhance material quality control in terms of materials. Sensors can be used, for instance, to track the composition of raw materials and find any variances or flaws that can affect the finished product. This information can be utilized to modify production procedures or discard products that don't satisfy quality requirements.
Challenges of Predictive Maintenance:
Even though implementing predictive maintenance in an industrial setting is unavoidable, several obstacles prevent its widespread use. Despite the existence of predictive maintenance algorithms, businesses looking to capitalize on Industry 4.0 must still weigh the advantages of predictive maintenance against the capital costs associated with purchasing the appropriate instruments, software, and knowledge:
-
Financial and Organisational
The anticipated expenses of any new investment must be considered for profitable businesses. The actions involved with predictive maintenance, including installing sensors, retrieving information, creating and maintaining models, and doing maintenance, can make a dent in the cost for the businesses that use them. The kind and complexity of the equipment and accompanying sensors, the price of consultation, installation, and knowledge extraction, and if the required expertise can be obtained internally or outside are just a few examples of the many variables that affect these expenses.
-
Data Source
The development of a production process management model requires the availability of pertinent data. Yet, businesses rarely introduce production process management with all the necessary data. The holes must be found and attempted to fill after using the data that is currently accessible. Moreover, the quality of the available information sources could not satisfy the requirements.
-
Highly Skilled Team
Although maintenance durations can be calculated by knowing how much longer a component has to live, there are still difficulties because of the need for human contact and the absence of self-maintenance. Keeping in mind that machine components now rely on human operators for control and maintenance, success depends on the caliber of human management and abilities.
Future of Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0:
As technology advances continue to produce new solutions for industrial processes, the future of predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0 appears bright. Predictive maintenance may be made even more efficient in identifying and diagnosing possible issues in industrial equipment with the use of machine learning and AI.
Predictive maintenance is projected to continue to advance significantly with the adoption of no-code platforms. These platforms enable users to build unique machine-learning models without substantial coding expertise. This could make it simpler for industrial operations to adopt and incorporate predictive maintenance technologies into their current workflows.
Overall, with continuous technological improvements and a rise in the acceptance of these solutions by industrial operations, the future of predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0 is promising. Reduced downtime, cheaper maintenance costs, and more effective resource utilization are just a few of the advantages that predictive maintenance will continue to offer, helping industrial organizations become more profitable and competitive.
